24 Jun

The accounting information became less valuable and incomparable due to the many accounting policies and the accounting treatment of transactions and occurrences. Therefore, to give accounting statements the quantitative characteristics of dependability, relevance, understandability, and comparability, people started to consider a set of minimal requirements that were universally applicable. IFRS and GAAP are two primary sets of rules accountants use to govern financial reporting globally. While every country has its unique financial reporting standards, these two are the most widely adopted standards around worldwide.
Table of Contents
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
IFRS is the acronym for International Financial Reporting Standards. IFRS is an international standard for financial reporting. In other words, it is a set of accounting principles and standards used to prepare a financial statement.
Companies that are on the list of exchanges, such as the London Stock Exchange, use IFRS. International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), an independent standard-setting body based in London, issued IFRS. It is a subsidiary of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO)
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
GAAP refers to common accounting principles, standards, and procedures used in preparing financial statements. In other words, GAAP are the accounting principles, standards, and procedures that businesses generally accept in a particular jurisdiction.
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) establishes GAAP. FASB’s responsibility is to establish accounting and financial reporting standards for businesses and charitable organizations in the United States. Furthermore, it is a nonprofit organization that operates independently.
Difference Betweeen IFRS and GAAP
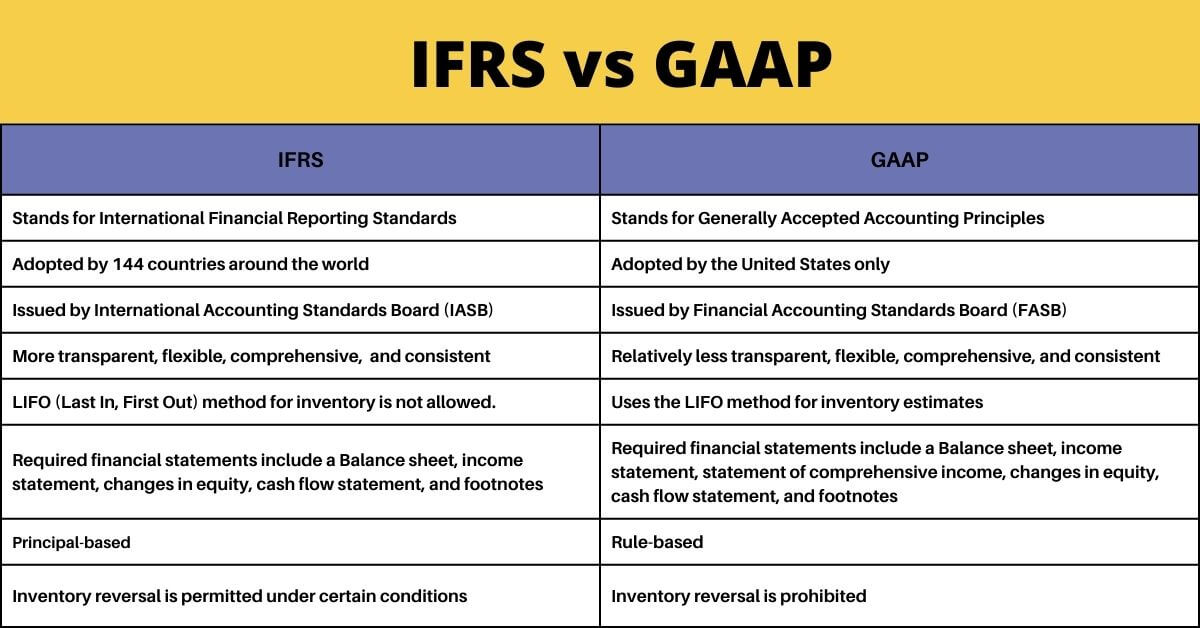
Despite many significant similarities, there are different ways in which IFRS and GAAP differ.
- As a general rule, IFRS is more prescriptive than GAAP. This means that the guidelines are more strict, and a company has fewer “creative” ways to account for its finances.
- IFRS is generally more international than GAAP because it must conform to the International Accounting Standards Board’s (IASB) standards.
- The accounting process is governed by precise rules and guidelines under GAAP, leaving minimal space for interpretation compare to IFRS.
- IFRS is more prescriptive, transparent, flexible, comprehensive, and consistent than GAAP.
- Liabilities are categorized either as current or non-current while preparing financial statements using GAAP accounting standards. However, in IFRS, businesses combine short-term and long-term liabilities since there is no clear line between them.
- While principles guide, GAAP is mostly rules-based. In essence, this means that IFRS Standards behave more like recommendations with flexibility for interpretation than GAAP Standards, which are more prescriptive and explicit.
Other common differences between are as follow:
Which Countries use IFRS and GAAP?
Some countries do not allow their companies to use US GAAP and instead require them to use IFRS. For example, countries like Japan, China, and India require companies to use IFRS as their standard financial reporting, while some countries like the US require GAAP. In addition, countries like Australia and the UK allow both.
Conclusion
Ultimately, IFRS vs. GAAP is a choice that each country has make on the basis of the accounting standards they want to follow. As we’ve seen here, each standard has different benefits and drawbacks. As a result, countries must decide which method they believe will best serve their financial markets to ensure all stakeholders have the essential information about a business’s finances.
Content writer at Invyce.com
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Meena Khan