06 May

Every company needs long-term growth and development but raising funds in the initial days is the biggest challenge for a company. Companies use various sources for raising funds like bank loans, personal investment, venture capital, shares, and debenture.
A debenture is the best option for raising funds through which companies raise money for long-term activities and growth. When the companies or governments want to raise their funds from the public, they issue debentures. It can be issued at a fixed rate of interest. So, this article unveils and gives you a clear understanding of the types of debenture and issuance.
Table of content
- What is a debenture?
- Types of debenture
- Issuance of debenture
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Key takeaways
What is a debenture?
Debenture comes from the Latin word “denture” which means borrow. A debenture is an investment issued by a business and organization to raise money for long-term growth and development. In other words, it is an agreement between the borrower and lender. The company borrows money from a lender at a fixed rate of interest called debenture interest, and the person holding the debenture is called the debenture holder. A debenture is a form of debt that is shown on the liability side of the balance sheet.
The company issued a promising note to the debenture holders to repay them their capital and fixed interest rate by a certain date.
Types of debenture
There are many types of debentures issues based on various factors. However, some of the most common types of debenture are:
- Based on convertibility
Convertible
The type of debenture in which investors have the right to convert their full debenture holding into the equity share company.
Non-convertible
A type of debenture that cannot be converted into an equity share.
- Based on Record
Registered
A type in which register debenture records in the register of debenture holders of the company. A transfer deed is required to transfer registered debentures.
Unregistered
An unregistered debenture is also known as a bearer debenture in the company. Unregistered debenture issued by companies allows their holders not to maintain any records. These debentures are transferred through delivery, which didn’t require a transfer deed.
- Based on performance
Redeemable
The type of debenture on which the expiry date is clearly mentioned on the company debenture certificate. In other words, redeemable debentures are issued for a specific time period. The company is bound to return the principal amount to the debenture holder on the expiry of the time period.
Irredeemable
The debenture has no fixed date regarding the payment to the debenture holders. These debentures are only paid back on the liquidation of the company.
- Based on security
Secured debenture
Security debenture carries a charge on the assets of the company. The debenture holder has the right to recover any principal amount or interest by liquidating the company’s assets in case the company fails to pay such an amount.
Unsecured debenture
An unsecured debenture is issued by a company that does not create a charge on the company assets. These debentures are issued solely on the basis of issuers’ trustworthiness or credibility.
- Based on priority
First debenture
A debenture that is repaid before other debentures is known as the first debenture
Second debenture
A debenture is paid after the first debenture, known as the second debenture.
Issuance of debenture
The issuing of debenture is much similar to the issuing of the shares by the company. In this procedure, the companies borrow funds at a fixed interest rate (debenture interest) and start releasing a prospectus declaring the debenture issuance for the interested investors. Interested investors apply for them, and the company issues debenture in one of the following ways at par, premium, and discount as explained under.
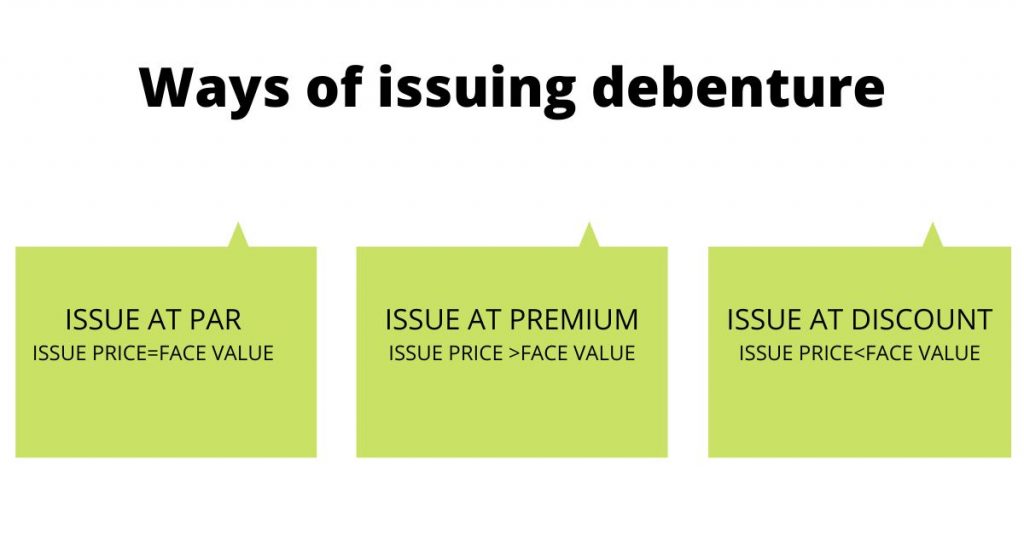
- Issue of debenture at par
In the debenture issue at par, the issue price is equal to its face value. In this scenario, the liabilities side is equal to the assets side.
- Issue of debenture at a discount
When the issue price is below its nominal value, It is said to be an issue of debenture at a discount.
For example
Rs 90 debenture issue at Rs 80, then Rs 10 is discount amount. In this condition, the balance sheet liabilities and assets sides do not match. This discounted amount of RS. 10 is a capital loss for a company that is treated as an asset and written off incoming financial periods.
- Issue of debenture at a premium
Debenture price is more than its nominal value, it is said to be an issue of debenture at a premium.
For example
Rs 100 debenture is issued for Rs 110, and Rs 10 is the premium amount. In this condition, again, assets and liabilities do not match. The premium amount of RS.10 is recorded under reserves and surplus in the balance sheet.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Issuing debenture is one of the effective ways to raise funds for the company’s long-term growth.
- Companies can easily redeem funds when they have enough funds.
- Debenture provides a fixed rate of interest to the lenders.
- It can encourage long-term funding to grow business.
- It can be advantageous during times of inflation.
Disadvantages
- A large amount of cash flow during the redemption process of debenture can negatively affect companies financial position.
- The lender loses their vote right and takes a share of the company’s profit by holding a debenture.
- Too much dependence on debenture can increase the financial risk for the company.
- A debenture is not a good investment choice in a low inflationary period.
- There is no flexibility in making a payment to the debenture holders.
Key takeaways
- A debenture is an investment issue by businesses and organizations to raise money for long-term growth and development.
- Debenture provides a fixed rate of interest to the lenders.
Shabana has been a committed content writer and strategist for over a 5 years. With a focus on SaaS products, she excels in crafting compelling and informative content.
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Shabana