13 Apr

Amortization is writing down the loan’s value and intangible assets like goodwill, trademark, copyright, etc. It is similar to depreciation, but this term is for intangible assets.
In amortization, only intangible assets can be amortized. However, if the intangible asset has an indefinite or unlimited lifespan, it can be amortized.
So, in this article, you will learn and understand the amortization, importance, and formula to calculate amortization.
Table of contents
- What is amortization?
- Accounting treatment for amortization
- How to calculate amortization expense?
- Amortization examples
- Importance of amortization
- Amortization VS Depreciation
- Key takeaways
What is amortization?
Amortization is a method of spreading the value of a loan and the cost of intangible assets over time. It may refer to two completely different financial processes: amortization of intangible assets and loans.
Amortization of intangible assets
Intangible assets are not physical, but they add value to your business. Examples of intangible assets are
- Trademark- A trademark is an intangible asset that prevents businesses from using business logos and names.
- Copyright- It is used to secure a business’s legal right to publish a work of authorship.
- Patents- It is a legal license that allows businesses to make, use or sell specific inventions.
- Goodwill- an intangible asset that is a company’s reputation that equals the acquisition price minus net assets.
- Franchises and license –It legally entitle a business to sell a product.
loans amortization
It refers to paying off debt over time in a regular installment of interest and outstanding loan principal. Examples of amortization loans are
- An auto loans-This loan is taken by the borrower to purchase a new vehicle.
- Student loans- An installment loan pays for college-related costs, including tuition, fees, and books.
- Home equity loans- A loan that allows homeowners to borrow against the equity in their homes. It is for those who want to use funds for home improvement projects.
- A personal loan- A loan is used for any legitimate financial need.
- Fixed-rate mortgages- A loan secured by real estate and has an interest rate that remains unchanged during the mortgage.
How to calculate amortization of loans
The formula to calculate a monthly principal amount due on the amortized loan is as under
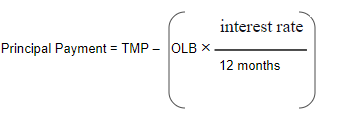
TMP= Total monthly payment
OLB=outstanding loan balance
Typically, If you want to calculate the total monthly payment, the formula will be as follow:
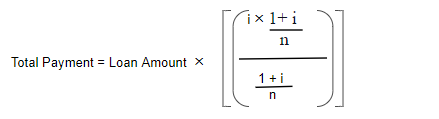
i=Monthly interest rate
n=Number of payments
Accounting treatment for amortization
The accounting treatment for amortization is similar to the accounting treatment of depreciation. Accumulated amortization is a contra asset that is why it is recorded in the balance sheet as it reduces the value of intangible assets shown on the balance sheet. Similarly, amortization expense is an income statement item so, it will be recorded as an expense in the income statement.
Let’s understand the accounting for amortization through example.
The ABC company has spent $200,000 to acquire a patent for 10 years. Therefore, It is an intangible asset and should be amortized over five years before its expiration. The entry to record amortization for each year would be:
| Debit | Credit | |
| Amortization expenses | 40,000 | |
| Accumulated amortization | 40,000 |
How to calculate amortization expense?
The following formula can calculate amortization expenses:
Initial value-residual value/ lifespan = Amortization expenses.
In this formula, you have to subtract the residual value of the assets from their initial value and divide them by the asset’s lifespan. If the asset has no residual value, divide the initial value by the life span. The result you can amortize each year.
Amortization examples
Let’s understand amortization through example.
Assume company XYZ purchases a patent for $10,000. The accountant recorded the patent in accounts at its cost value. So, It also determined the useful life of the patent to be 10 years.
At the end of the year, XYZ company records the amortization expense for the patent.
The amortization expense will be $2,000 ($10,000/10 years) each year. The company uses a double-entry system under:
Amortization expenses=Initial value-residual value/ lifespan
10,000/10
Amortization expenses = 1,000
NOTE: In the above example the asset has zero residual value so we divide the initial value by lifespan.

Importance of amortization
Amortization helps in managing the intangible asset of the business. It is crucial because it assists investors and businesses in understanding and forecasting their costs on time.
In addition, this can be useful for deducting interest payments for tax purposes. Moreover, it can reduce a business’s taxable income and tax liability while giving investors a better understanding of the true learning of the company.
Amortization VS Depreciation
| Amortization | Depreciation |
| Amortization is a method of spreading the cost of intangible assets over the asset’s useful life cycle. | Depreciation refers to expensing fixed assets (tangible) over their useful lifecycle. |
| It is used for intangible assets such as trademarks, Goodwill, and copyright. | It is used for tangible assets including vehicles, machines, and computers. |
| Amortization calculation does not usually salvage value(resale value) once its useful life has expired. | A tangible asset may have some salvage value, so this amount is more likely to be included in a depreciation calculation. |
| Amortization can be done through the straight-line method. | In contrast, depreciation of tangible assets can be done through a straight line or accelerated depreciation method. |
| The formula of amortization: Annual amortization=(Cost of intangible assets)/ useful life | The formula of depreciation: Annual depreciation =(Cost of tangible assets-salvage value)/useful life |
Key takeaways
- Amortization is a technique used to spread the cost of an intangible asset and loans over a period.
- Amortization is similar to depreciation but this term is for intangible assets.
- and it helps in managing the intangible assets of the business.
- In addition, it assists businesses and investor in understanding and forecasting their cost on time.
- Moreover, it can be useful for deducting interest payments for tax purposes.
Shabana has been a committed content writer and strategist for over a 5 years. With a focus on SaaS products, she excels in crafting compelling and informative content.
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Shabana