14 Mar

The unadjusted trial balance is the fourth crucial step of the accounting cycle. An unadjusted trial balance is prepared after posting entries into the general ledger to proceed with the accounting cycle/process. The primary purpose is to detect mathematical errors, accuracy and provide the basis for financial statements.
This article provides information about prepare unadjusted trial balance, why it is prepared, and errors that an unadjusted trial balance fails to detect.
Table of Contents
What is a trial balance?
An unadjusted trial balance or trial balance is listing all account balances to create a financial statement before adjusting entries are made. It is prepared on a monthly, quarterly, and yearly basis. Moreover, it helps to detect errors and make sure that all debit and credit balances should be equal .
The Unadjusted trial balance can be prepared by many software packages and also manually.
Why the unadjusted trial balance is prepared
There are various purposes for preparing a trial balance. However, the trial balance is the foundation for the preparation of financial statements.
Let’s dive into the detailed purposes of trial balance.
Reference for financial statement
The main purpose of the trial balance is to use it as a reference for the preparation of the financial statement.
Identify errors
The trial balance detects the errors quickly by matching the debit and credit totals. If the total credit and debit balance are not equal, there may be an error.
To check mathematical accuracy.
Trial balance ensures that the balances are mathematically correct. In addition, it provides us with the total credit and debit balances.
Summarize Balances
A trial balance summarizes all the debit and credit balances.
Provide a basis for adjustment
An unadjusted trial balance provides the basis for adjusting entries by making a list of all accounts that may need adjustments.
For management use
The trial balance gives an accurate report of available cash, revenue level, debit, and credit status.
Format of unadjusted trial and balance
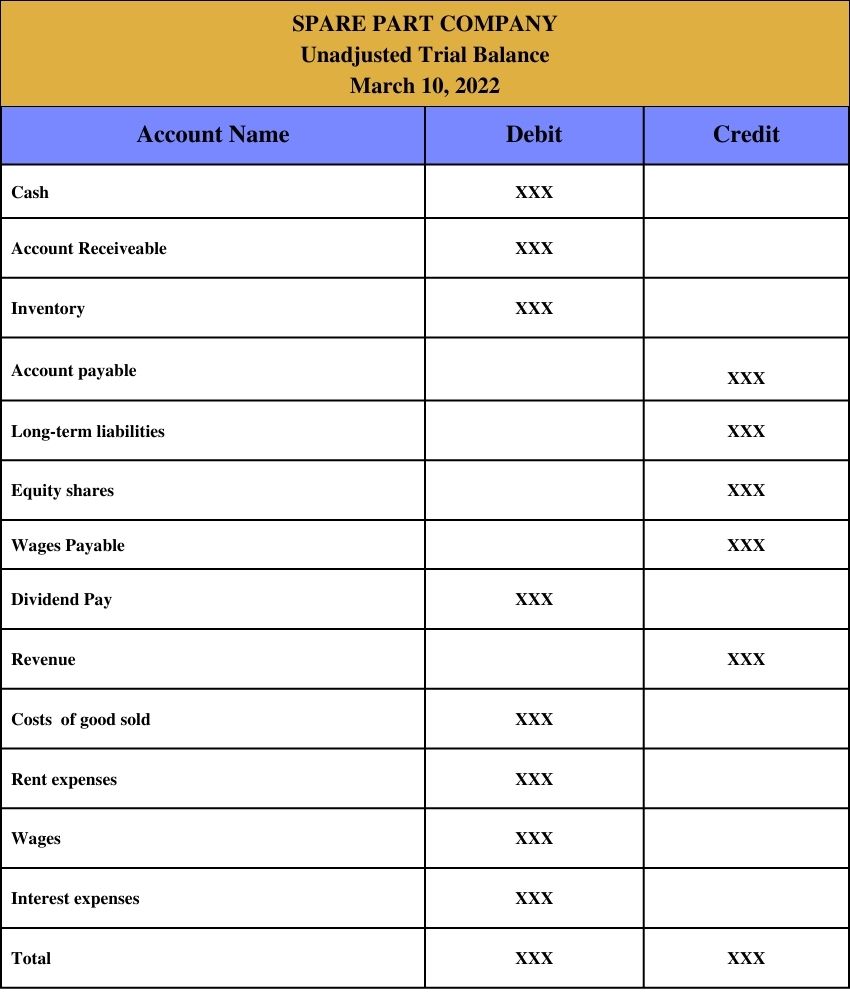
The unadjusted trial balance contains three columns: account name, debit, and credit.
In the unadjusted trial balance, the total debit equals the total credit. Both debit and credit accounts are calculated at the bottom of the trial balance. If the totals aren’t the same, there may be two reasons: the trial and balance have been prepared incorrectly, or journal entries have not been correctly transferred into the ledger account.
A full format of the unadjusted trial balance is given below:
How to prepare an unadjusted trial balance
- The first step of preparing an unadjusted trial balance is making a format: one column for the account name, the second column for debit, and the third for credit.
- After preparing the format take the balances from the general ledger and record them into the unadjusted trial balance
- Then write the balances in respective debit and credit columns.
- Calculate the total balance of the debit and credit side
- Make sure the total of both credit and debit sides is mathematically correct. If the error occurred, identify reasons for errors and correct them.
Examples of unadjusted trial balance
Examples of the unadjusted trial balance are the following:
Example# 1
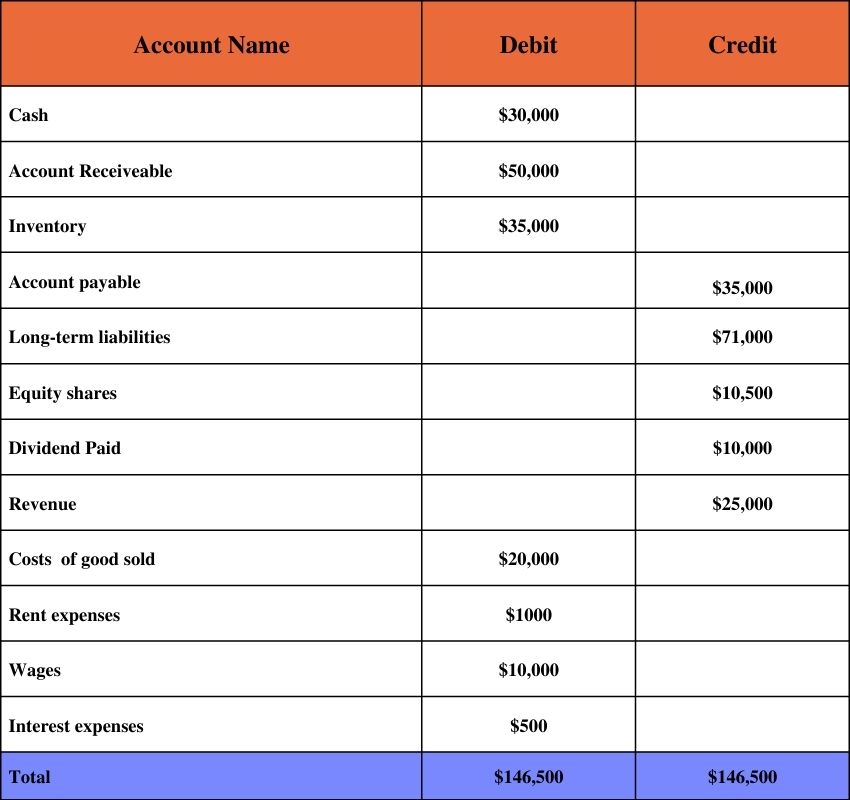
A company trading spare parts want to make a trial balance from the below ledger balance-Cash $30,000, account receivable $50,000 inventory $35,000, account payable $35,000,equity share $10,500,cost of goods sold $20,000,wages $10,000, long term liability $71,000, dividend paid $10,000, revenue $25,000,rent expenses $1000,interest expenses $500.
The unadjusted trial balance is as under.
Example # 2
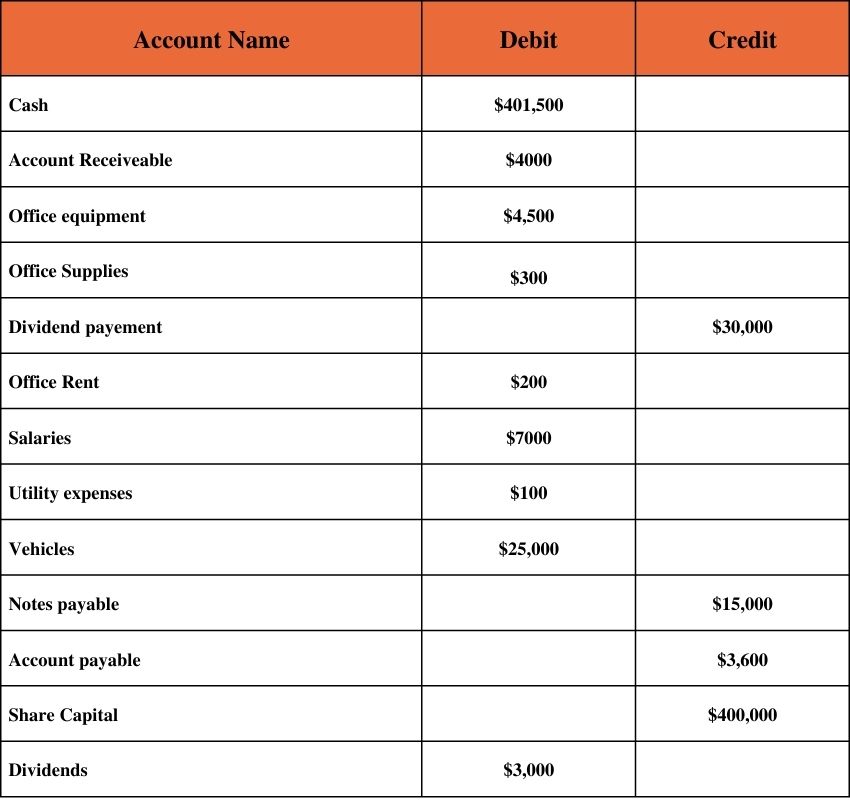
Suppose an XYZ company prepares an unadjusted trial balance from the ledger account. The unadjusted trial balance is as below:
What if unadjusted trial balance do not balance
If the unadjusted trial balance is equal, the accountant can proceed to the next step of the accounting process/cycle. But if a problem is discovered with the trial balance, it isn’t easy to proceed further. So finding and fixing an error is crucial to moving further. The error may occur in preparing journal entries, posting accounts to the general ledger, or it may be while preparing a trial balance. That’s the primary task of an accountant to find out where the error occurs and fix it before proceeding to the next steps.
Errors that trial balance fails to detect
There may be some errors that the unadjusted trial balance fails to detect.
Posting to the wrong account
An error can occur when posting an item to the wrong account but on the right side. Thus, the trial balance will not detect such errors.
An error of principle
If a transaction is incorrectly recorded in the journals, such as recording purchase inventory as supplies.
Compensating errors
In this kind of error, if one account in the ledger is debited Rs1000 less and another account in the ledger is credited Rs1000 less, these errors cancel themselves. A similar error neutralizes one error on the opposite side.
Error in debit and credit
If the debit and credit are recorded incorrectly, there is an error.
Conclusion
An unadjusted trial balance is crucial for making a financial statement. This article will help you better understand the unadjusted trial balance and your business financial condition.
Shabana has been a committed content writer and strategist for over a 5 years. With a focus on SaaS products, she excels in crafting compelling and informative content.
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Shabana