25 Jul

Issuing debt securities for investors to buy is one of the most efficient tools the government has at its disposal when it wants to generate money. Both government bonds and treasury bills fall under this category. This article will help you to learn more about treasury bills.
Table of Contents
What are Treasury Bills?
Treasury bills are short-term debt obligations issued by the government. They may also be called “notes” or “bills.” You can sell T-bills at a discount to par value, which means they pay no interest. Instead, you pay only what it costs to buy the bill. They mature in one year or less from the date of issuance, offering investors a risk-free way to park cash for short periods. While some treasury bills have a maximum denomination of $5 million, most are sold in denominations of $1,000.
Background
In order to balance the nation’s historically high public debt, treasury bills were initially employed in the United States during World War I as a source of emergency funding. T-bills were the most widely used type of short-term government security towards the end of World War II.
Purpose of Treasury Bills
Treasury bills serve several purposes. Some are as follows;
- To provide cash flows needed for current operations.
- To ensure that there is enough money available at times of need.
- T-bills make it easier for businesses and individuals who want loans over more extended periods than otherwise. This is important if you want a loan with low-interest rates.
How Do T-bills work?
Treasury notes are genuinely worth the amount specified on their face value. However, you can purchase them for less. For example, the government issue a bill of worth $2000. If you want to purchase it, you will pay $1900. Every bill has a maturity date corresponding to the time you get your money back. Following that, the government pays your payment in full, $2000, and you receive $500 in return for your investment. Your income is regarded as interest or repayment for your funds’ loan. The discount rate that is expressed as a percentage is the difference between the bill’s value and the amount you pay. The discount rate in the scenario mentioned above is 5%.
How to Purchase Treasury Bills?
You can buy treasury bills by any of the following methods;
Competitive Bidding
In this type of bidding, investors purchase t-bills at a particular discount rate that they are ready to accept. Each bidder’s or investor’s lowest rate or discount margin acceptance is stated in the bid. The lowest discount rate-accepting bids are accepted first. Bids at the next lowest rate are allowed if there aren’t enough at that level to fill the issue completely. Up until the entire issue has been sold, the process is repeated. A broker or a bank must be used to make the purchase payments.
Non-Competitive Bidding
In a non-competitive bid, the investor accepts the auction’s chosen discount rate. The average price for T-bills sold at auction is the yield that an investor obtains. Since they are assured of receiving the entire bill amount at the end of the maturity period, individual investors prefer this strategy.
Secondary Market
Investors can also purchase t-bills from the secondary market. In the secondary market, other investors who want cash sell these bills at a discount rate while other investors buy from them.
What Determines the T-bills price?
The following are few of the many variables that may affect the cost of Treasury Bills:
- Government’s monetary policy, such as Federal interest rates.
- Maturity duration, with higher rates of return available for longer maturities
- Macroeconomic conditions, with riskier markets and more volatile markets
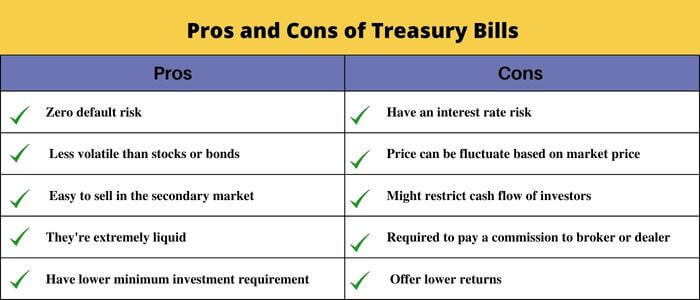
Pros and Cons of Treasury bills
Following are pros and cons of t-bills.
Pros
- The pros of treasury bills are that they’re extremely liquid. In other words, you can get your money out quickly, within minutes or even seconds if you want to.
- They’re also fairly safe investments and tend to be less volatile than stocks or bonds. That means that the value of a Treasury bill won’t fluctuate as much over time as it would with other types of investments such as stocks or bonds.
- Finally, they’re usually easy to sell in the secondary market if you need more cash immediately. You just have to go through an agent who handles sales like any other sale on Wall Street.
Cons
- You can purchase T-bills from a broker or dealer, but you might be required to pay a commission.
- They mature so quickly that you must constantly turn them into fresh ventures.
- No matter what you paid for your bond when you purchased it, the price will fluctuate periodically based on market interest rates. Hence there is always a risk of increasing interest rates.
- T-bills might restrict cash flow for investors who need a consistent source of income.
Key Takeaways
- A Treasury Bill (T-Bill) is a short-term debt obligation with a maturity of one year or less issued by the government.
- Treasury notes are genuinely worth the amount specified on their face value.
- You can buy t-bills by competitive bidding, non-competitive bidding, or secondary market.
Content writer at Invyce.com
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Meena Khan