09 Feb

Whether you are a student or owner of any business, you need to learn account basics. This quick guide will help you understand accounting basics.
Let’s for it…
What is accounting?
Accounting is the language of business that gives an overview of business finance. It is a comprehensive system to collect, analyze and communicate business financial data. In other word, Accounting is the art of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial data .
Accounting objectives

The following are the main objectives of accounting.
Keep systematic recording.
Accounting is done to keep a systematic record of financial data. The primary function of accounting is to systematically record financial data to drive the correct and valuable results of financial statements.
To ascertain profit and loss.
Another objective of accounting is to evaluate the profit and loss of the business and can easily determine the company’s profit and loss.
To ascertain financial positions.
Accounting helps businesses to know about their financial position. In accounting, the balance sheet serves as a tool for ascertaining the business’s financial health.
Provide accounting information to interested parties.
Accounting aims to give accounting information to interested parties like bankers, creditors, and tax authorities. It enables interested parties to make sound and realistic decisions.
Ascertain the financial result.
The accounting objective is to determine the exact status of your company’s financial health at the end of a particular period.
Detection and prevention of fraud
The accounting objective is to protect a company from fraud and mismanagement by recording accurate and actual transactions.
Basics Accounting Concept

The main objective of the accounting concept is to maintain consistency in the accounting records. All accounting concepts have been developed over the years from experience, and thus, accounting concepts are universally accepted. The following are the accounting concepts:
Basic entity concept
According to this concept, business and owner are two different independent entities. Therefore, the business and owner’s transactions should be recorded separately. Thus, the business has its own identity. For example, suppose an owner takes cash of 1000 from a business for domestic purposes. It is considered a drawing. “Drawing is a withdrawal of cash or goods by the owner from the business for the purpose of personal usage.”
Money Measurement Concept
This concept concludes that all business transactions must be in the form of money in the country’s currency. For example, such transactions are in Pakistan in rupees, and in America, business transactions are in dollars
Going Concern Concept
This concept states that every business entity has continuity of life. We should remember that business is a going concern and that the business will continue operations for an infinite period. Suppliers will not provide goods or services if any business neglects the concept of going concern. Banks will not provide a loan, and employees will not work correctly.
Going Concern Concept
The accounting period is a fixed time period during which all economic transactions of the business are recorded, accounting period may be monthly, quarterly, or yearly according to business needs and requirements. The ultimate aim of the accounting period is to provide details of business performance to interested parties like investors, bankers, creditors, suppliers, etc.
During the accounting period, financial statements are prepared to identify profit and loss that occur during a financial period, based on which future strategies are established to improve performance in the future.
Accounting Cost Concept
This concept states that all assets are recorded in the book of accounts at a cost at which the asset is purchased irrespective of its market price. The cost of assets includes all the expenses incurred from purchase till installation, i.e., tax, transportation, labor, and installation.
Duality Aspect Concept
The dual aspect concept assumes that every financial transaction has a dual effect. It affects the two accounts on their respective opposite sides.
For example, goods purchased for cash have two aspects;
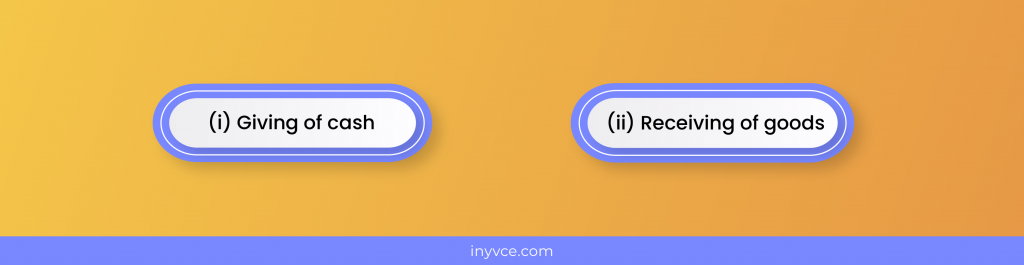
Thus, the dual concept is expressed in terms of a fundamental accounting equation;

Accrual Concept
The accrual concept determines the amount of money that is yet to be paid or received at the end of the accounting period. Accrual-based accounting allows you to record economic transactions as soon as a transaction occurs. You don’t need to wait to record a transaction till payment is made for expenses or cash received for the sale of goods or services.
In books of accounts, the amount yet to be paid is recorded in the balance sheet under accounts payable, considering it a current liability. Similarly, the amount yet to be received is recorded in the balance sheet under accounts receivable, considering it as a current asset.
Matching Concept
Matching concept based on accounting period concept. The expenditure of a firm for a particular accounting period is to be compared with the revenue of the same accounting period to determine the accurate profit and loss of a firm for the same period.
Types of accounting

There are three main types of accounting.
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting is a process used to generate interim and annual financial statements. All financial transactions are summarized in a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of retained earnings.
Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting is the same as financial accounting but organizes and summarizes data differently. In addition, it covers many other facets of accounting, including budgeting, forecasting, and various financial analysis tools.
Cost Accounting
Cost accounting helps businesses to make decisions about costs. It considers all of the costs related to producing a product. Business owners, managers, and accountants use this information to determine what their products should cost. In cost accounting money is cast as an economic factor in production.
Accounting cycle

The accounting cycle refers to all accounting tasks involved in completing an accounting process. The length of the accounting cycle can be monthly, yearly, and quarterly.
Let’s discuss the accounting process step by step.
Collection and analysis of documents
In this step, the accountant examines the source documents and analyzes them. This is a continual process throughout the accounting period. An accounting process starts when a business transaction occurs—for example, sales, purchases, bank-related documents, etc.
Recording in journal
Based on the above documents, accountants pass journal entries using the double-entry system (debit and credit). This process also continues throughout the accounting period.
Ledger Account
This is also a continuous process in the accounting period. In this process, all accounts are gathered in a concerned ledger account. A ledger is a summary of all past transactions of a company and includes all the debit and credit transactions affecting a concerned account.
Trial Balance
Accountants prepare trial balances at the end of each accounting period. Usually, it summarizes all the balances of ledger accounts irrespective of whether they carry a debit or credit balance. Through trial balance, the accuracy of the ledger is determined when its debit and credit sides tally with each other.
Adjusting Entries
This process is performed at the end of an accounting period. Adjusting entries are passed to update expense and revenue accounts to fulfill the matching principle of accounting and rectify any errors made in previous journal entries. These entries are first passed through the journal, posted in ledger accounts, and finally in the trial balance.
Adjusted Trial Balance
The accountant creates an adjusted trial balance based on the above adjustment entries. It is a platform for preparing the financial statement of the company.
Preparation of Financial Statement
A financial statement clearly shows the financial health of the company. It is the statements like cash flow, cash fund, profit and loss, and balance sheet.
Post-closing Entries
In this process, certain accounts are closed, so they have zero balance at the beginning of the new accounting period.
Post-closing Trial Balance
The last step of the accounting process represents the balance of expense, revenue, asset, liabilities, and capital account. Then these balances are transferred into the next financial year as an opening balance.
Basic Accounting Terms

Accounting terms are universal. These terms help you understand accounting deeply.
Account Payable
This accounting term refers to the money due on a company because of goods or services received, but payment is not made yet. These are the owners owed to the vendors, bondholders, and suppliers.
Account Receivable
Account receivable is the opposite of account payable; it’s what the customers owe the owner to consume goods and services.
Equity
Equity is also known as “owners equity.” Equity refers to the amount of money invested in a business by its owners.
It can also include a non-momentary value such as energy, time, and other resources.
Expenses
Expenses refer to “The cost of doing business” or any purchase you make or money you spend.
Fiscal Year
The fiscal year is a period that companies use for accounting. This period varies from one company to another. Some follow the calendar year, while others see the financial statement.
Liabilities
Liabilities are everything that companies owe for the short and long term. Liabilities include all payroll, taxes, loans, and credit cards.
Depreciation
The depreciation term allocates the cost of tangible and physical assets over their useful life or life expectancy.
Burn Rate
Burn rate is an accounting process that refers to how quickly your business spends money. It is a critical process while managing and calculating cash flow.
Capital
Capital refers to the money that the owner invests in your business.
Revenue
Revenue is the total amount you earn on selling your products and services before expenses are taken out.
Profit
In accounting, profit refers to the “financial advantage or benefits.” It is the difference between income expenses and COGS(Cost of goods sold)
Costs of goods sold(COGS)
This term refers to the production cost of your product and service. It is also known as cost of sale(COS). It is the expense you will see on the profit and loss statement.
Accrual
Accrual refers to expenses that were already recorded but not yet paid.
Gross Margin
Gross margin is also known as gross income. It is minus your total sale to COGS, indicating your business sustainability.
Basic Accounting Principles

Accounting principles are rules companies, and accountants must follow while calculating financial data. The following are the principles that help companies and accountants to develop their financial reports and data accurately.
Periodicity Principle
This principle states that all accounting entries should be reported in relevant periods. For example, all expenses and revenue should be reported in the relevant accounting period.
Principle of Prudence
This principle states that financial data should be presented based on factual information, not speculation.
Principle of Sincerity
According to this principle, the accountant should present all financial information fairly and accurately.
Principle of Permanence
This principle states that all financial reporting and data should be consistent across periods.
Principle of Materiality
According to this principle, an accountant should fully disclose all financial data in the financial report.
Principle of Continuity
This principle states that the company should continue operations. That means the company’s future should align with what happened in the past.
Principle of non-compensation
Principle of non-compensation states that both negative and positive financial data should be reported with full transparency.
Principle of regularity
The principle of regularity states that accountants should strictly follow the regulations and standards of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Golden Rules of Accounting

Three golden rules of accounting keep your account book up-to-date and accurate. The following are the three basic rules of accounting.
Debit the receiver and credit the giver
This rule of debiting the receiver and crediting the giver applies to a personal account. If you receive something, debit the account, and give something credit to the account.
Debit what comes in and credit what goes out
The rule applies to real accounts. It covers all accounts related to the asset, liability, and equity accounts. This consists of tangible and intangible real accounts.
This rule debits the account when something comes into your business and a credit account when something goes out of your business.
Debit all expenses and losses and credit all gains and income
The third rule of accounting deals with nominal account/temporary accounts. These accounts include expenses, losses, gains, and revenue. It closes at the end of each accounting period.
In nominal or temporary accounts, if your business has a loss or expenses, it debits your accounts; conversely, credit your account if your business has a gain or revenue.
Accounting Equations
The accounting equation states that the total company’s assets equal the sum of its liabilities and shareholder’s equity. The accounting equation ensures the balance, so each entry encoded on the debit side should have related coverage on the credit side. The balance sheet is the basis of the accounting equation.
Three factors make up the accounting equation:

Conclusion
This guide spotlights accounting objectives, types, golden rules, terms, cycle, concepts, principles, equations, and conventions. I hope this accounting guide helped you in understanding accounting.
Accounting can help business owners better understand their financial position and allocate their budgets more wisely.
Shabana has been a committed content writer and strategist for over a 5 years. With a focus on SaaS products, she excels in crafting compelling and informative content.
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Shabana