01 Nov

Do you know what an employee stock option plan (ESOP) is? Do you understand how it functions and how it might help you as a worker? This blog post will explore everything you need to know about employee stock option plans, how they work, and what benefits they offer. So read on to learn more about ESOPs and whether or not they are right for you.
Table of Contents
What is an Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP)?
An employee stock option plan is a benefit plan that gives employees the right to purchase company stock or shares at a predetermined price. The price is typically set at the stock’s fair market value on the date the shares are granted. Employees may be interested in purchasing these shares because the company offers these shares at a discounted price. Hence, obtaining such an opportunity can reap handsome return and gives employees a feeling of ownership.
ESOPs are intended to incentivize and retain employees by giving them a stake in the company’s success. When the company does well, employees can reap the financial rewards through increases in the value of their stock holdings. ESOPs can also help attract and retain top talent, as prospective employees are often attracted to companies that offer this type of benefit.
Process Of Issuing ESOP
The process of issuing ESOPs is relatively simple. First, the company must determine the number of shares set aside for the plan. This can be done by considering the percentage of ownership that the employees should have. Once this has been decided, the company needs to set up a trust or holding company that will manage ESOPs on behalf of the employees.
The next step is to issue the ESOPs to the employees. This can be done through various methods, such as giving each employee a certain number of shares or offering them the opportunity to purchase shares at a discount. When employees who are ESOP participants want to exit or retire from the company, they receive their equity on their departure. Some companies repurchase the leaving employee’s shares at fair market value.
To Whom Can The ESOP Be Issued?
An employee stock option plan (ESOP) can be issued to any company’s eligible employees. To be eligible for an ESOP, an employee must be;
- Permanent employee of the company working in or outside a country.
- Hard-working and active employee
- Have completed a specified service period with the company. This period is typically one year but may be longer or shorter depending on the company’s internal policies.
Types of Employee Stock Option Plan
There are four types of employee stock option plans: Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP), Employee Stock Option Scheme (ESOS), Restricted Stock Units (RSU), and Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs).
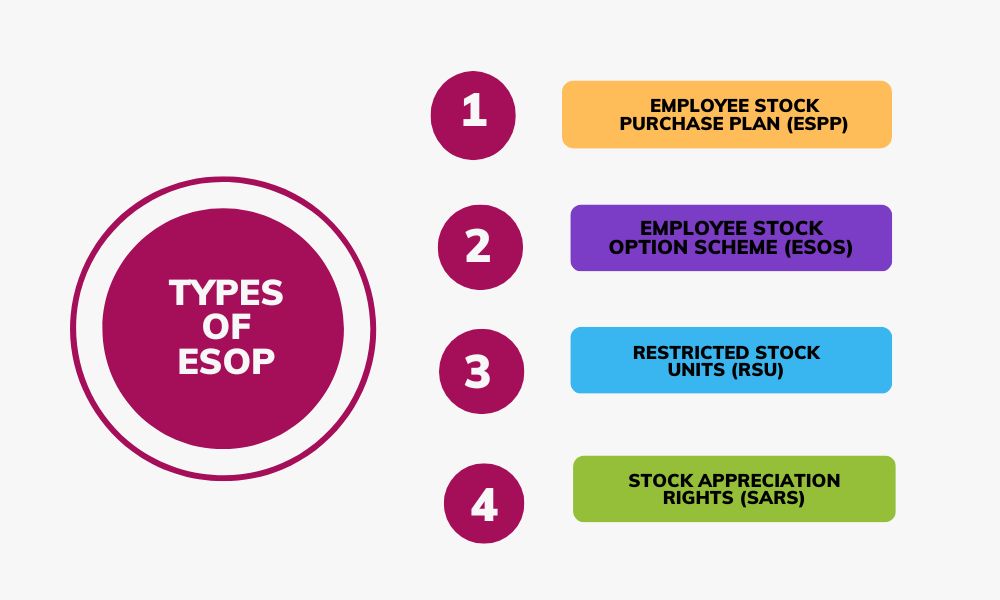
Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP)
ESPPs are issued to employees who completed a minimum service period. Employees can buy the company’s shares through employee stock purchase plans, frequently for less than fair market value. The duration and cost of the Employees’ ownership of Company shares are outlined in the Plan’s terms. ESPPs are typically designed to provide shares as a component of public issues.
Employee Stock Option Scheme (ESOS)
This involves giving the employee options based on a predetermined valuation that is limited by a vesting schedule and performance criteria. The employee may exercise options to acquire shares after the vesting period has passed by paying the specified exercise price.
Restricted Stock Units (RSU)
In this type, shares in the company are only given to the employee upon the occurrence of an event. The employee only becomes a stakeholder following a predetermined event or satisfying specific conditions.
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs)
SARs give employees cash payouts equating to the growth in the company’s shares over a predetermined period of time. SARs offer employees equity upside without any downside exposure, in contrast to other choices.
Advantages Of ESOP
An employee stock option plan can offer several advantages to employees and employers.
Increase employees’ motivation: An ESOP can provide a way to own a stake in the company they work for, leading to increased motivation and job satisfaction. In addition, an ESOP can provide a financial incentive to stay with a company for the long term, as options typically vest over several years.
Tax benefit: Another advantage of ESOP is that it provides employee tax benefits. An employee does not need to pay tax on these shares. They only pay tax at the time of receiving shares or when they leave a company before retirement.
Increases company’s performance: An ESOP can help employers retain key employees and attract new talent. In addition, ESOP can be used to motivate and reward employees for their performance which ultimately improves the performance and positive outcome of the company.
Disadvantages Of ESOP
There are a few disadvantages to implementing an employee stock option plan (ESOP).
- Setting up and administering the employee stock option plan is costly. This can be significant, especially for small businesses.
- When a company provides ESOP, the employees only depend on one company for their salaries and other benefits. As a result, employees’ investments could be worthless if the company goes bankrupt or is bought out.
- There is the risk that employees will not purchase shares or will purchase and then sell the stock immediately, resulting in no long-term benefit to the company.
- There is the potential for abuse of the system by employees who can manipulate the timing of their options exercises to maximize their benefits at the company’s expense.
- Once ESOPs are issued, this can increase outstanding shares, decreasing earnings per share(EPS).
Conclusion
An employee stock option plan is tool companies use to entice top talent to join their company. Compared with other types of equity compensation, employee stock options have a few distinct advantages. However, it’s important to remember that this tool is only suitable for some companies or situations. By assessing your own company’s position and determining whether board approval is likely, you can decide whether you should pursue options as a part of your company’s equity compensation program.
Content writer at Invyce.com
Related Post
Copyright © 2024 – Powered by uConnect



Meena Khan